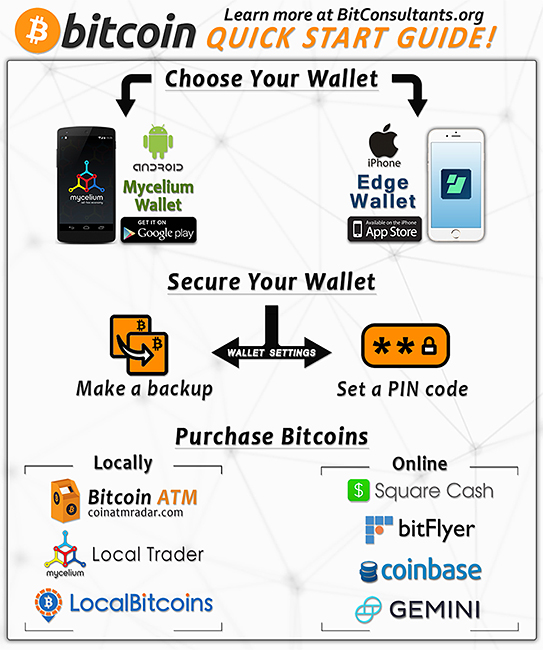
What is Bitcoin?
What Makes Bitcoin Unique?
1. A technological breakthrough: Bitcoin solves a computer science problem known as the double-spend problem and acts as the first triple entry accounting system to exist on a global scale. It has become the most successful and robust digital currency system in existence.2. Limited supply: Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist; this number is hard-coded into the software and cannot be changed without consent from the network majority. Bitcoins aren’t printed like dollars or euros – they exist digitally and are distributed by the Bitcoin software at a predetermined rate. The software rewards bitcoins to users who contribute their computing power to support the network.
3. Transparency: Every bitcoin transaction in the network is accounted for, agreed upon, and recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is viewable by anyone. The blockchain requires no personal identity information, and thus provides a strong level of financial privacy.
4. Security and control: Bitcoin users are in full control of their assets at all times; all transactions must be initiated by the user. You have complete control over your bitcoins; no bank, government, or corporation can censor how or when you use them. Bitcoin transactions are made without the need for personal information and protect against any possible identity theft. Bitcoin users can also secure their funds with passphrases and offline backups, making bitcoin one of the most secure assets in existence.
5. No central authority: Bitcoin is not a company -- it is a decentralized network that operates on consensus. Because the Bitcoin network has no central authority, it is virtually impossible to shut down, outside of shutting down the entire internet. Bitcoins cannot be artificially created; the bitcoin supply is mathematically regulated by the protocol.
6. Reduced risk for businesses: Bitcoin transactions are secure, irreversible, and do not contain customers’ financial or personal information. This protects businesses from risks like identity theft or fraudulent chargebacks, and does not require PCI compliance. Businesses can easily expand to new markets where credit cards and PayPal are not available or fraud rates are unacceptably high. The net results are: lower fees, larger markets, and fewer administrative costs.
7. Payment freedom: It is possible, with Bitcoin, to send and receive any amount of money, instantly, anywhere in the world at any time -- no bank holidays, no borders, no imposed limits. Bitcoin creates a global free market that allows its users to be in full control of their money.
8. Speed: Transactions happen instantly and are confirmed in 10 minutes, on average. Bitcoin transactions are faster, safer, and cheaper than any traditional bank or wire transfer.
9. Low fees: The Bitcoin network bears very low transaction fees, (currently a few pennies). Fees are optional, but they do determine how fast your transaction is processed. These fees are paid directly to miners to help secure the network.10. No barriers: Bitcoin is an open protocol and has no barriers to entry. Anybody can download the free software and join the network.
11. A digital commodity: Bitcoin’s value is determined strictly by supply and demand. Since Bitcoin is relatively new and sometimes misunderstood, the price can be volatile in the free market. As the technology becomes more widespread and trusted, the volatility should naturally decrease.
12. Versatility, openness, and vibrancy: The open-source nature of Bitcoin encourages broad innovation, and has created a thriving new economy that is quickly outpacing many countries.